Sunday, 15th February 2026
Launching Interop 2026. Jake Archibald reports on Interop 2026, the initiative between Apple, Google, Igalia, Microsoft, and Mozilla to collaborate on ensuring a targeted set of web platform features reach cross-browser parity over the course of the year.
I hadn't realized how influential and successful the Interop series has been. It started back in 2021 as Compat 2021 before being rebranded to Interop in 2022.
The dashboards for each year can be seen here, and they demonstrate how wildly effective the program has been: 2021, 2022, 2023, 2024, 2025, 2026.
Here's the progress chart for 2025, which shows every browser vendor racing towards a 95%+ score by the end of the year:
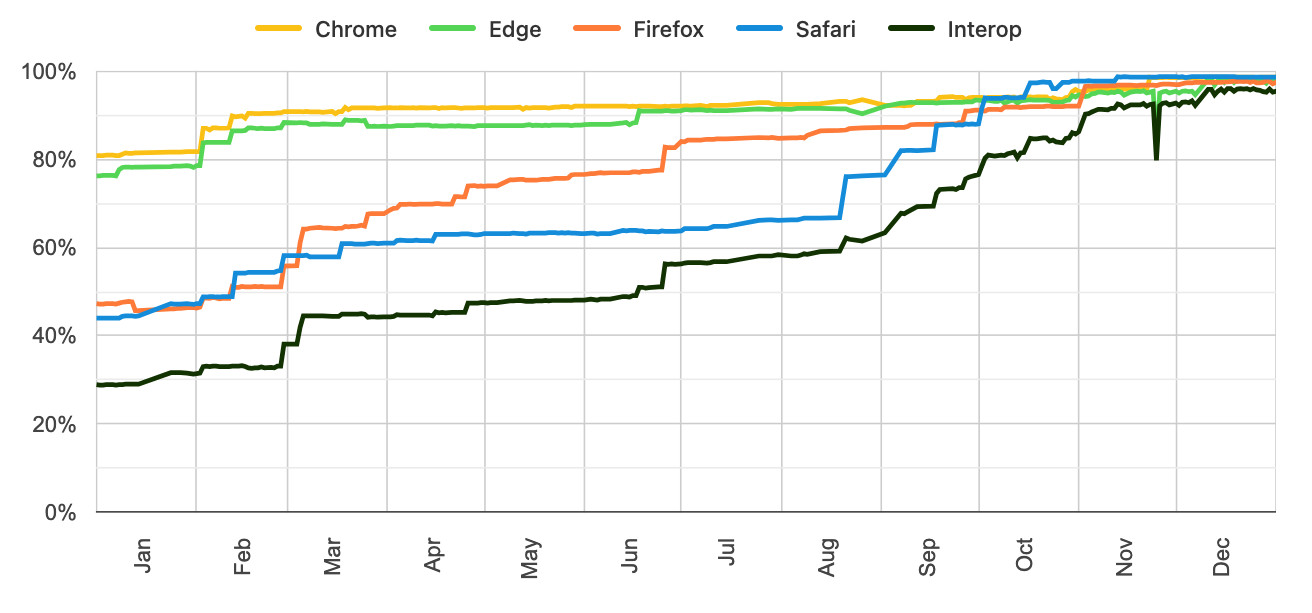
The feature I'm most excited about in 2026 is Cross-document View Transitions, building on the successful 2025 target of Same-Document View Transitions. This will provide fancy SPA-style transitions between pages on websites with no JavaScript at all.
As a keen WebAssembly tinkerer I'm also intrigued by this one:
JavaScript Promise Integration for Wasm allows WebAssembly to asynchronously 'suspend', waiting on the result of an external promise. This simplifies the compilation of languages like C/C++ which expect APIs to run synchronously.
How Generative and Agentic AI Shift Concern from Technical Debt to Cognitive Debt (via) This piece by Margaret-Anne Storey is the best explanation of the term cognitive debt I've seen so far.
Cognitive debt, a term gaining traction recently, instead communicates the notion that the debt compounded from going fast lives in the brains of the developers and affects their lived experiences and abilities to “go fast” or to make changes. Even if AI agents produce code that could be easy to understand, the humans involved may have simply lost the plot and may not understand what the program is supposed to do, how their intentions were implemented, or how to possibly change it.
Margaret-Anne expands on this further with an anecdote about a student team she coached:
But by weeks 7 or 8, one team hit a wall. They could no longer make even simple changes without breaking something unexpected. When I met with them, the team initially blamed technical debt: messy code, poor architecture, hurried implementations. But as we dug deeper, the real problem emerged: no one on the team could explain why certain design decisions had been made or how different parts of the system were supposed to work together. The code might have been messy, but the bigger issue was that the theory of the system, their shared understanding, had fragmented or disappeared entirely. They had accumulated cognitive debt faster than technical debt, and it paralyzed them.
I've experienced this myself on some of my more ambitious vibe-code-adjacent projects. I've been experimenting with prompting entire new features into existence without reviewing their implementations and, while it works surprisingly well, I've found myself getting lost in my own projects.
I no longer have a firm mental model of what they can do and how they work, which means each additional feature becomes harder to reason about, eventually leading me to lose the ability to make confident decisions about where to go next.
I saw yet another “CSS is a massively bloated mess” whine and I’m like. My dude. My brother in Chromium. It is trying as hard as it can to express the totality of visual presentation and layout design and typography and animation and digital interactivity and a few other things in a human-readable text format. It’s not bloated, it’s fantastically ambitious. Its reach is greater than most of us can hope to grasp. Put some respect on its name.
It's wild that the first commit to OpenClaw was on November 25th 2025, and less than three months later it's hit 10,000 commits from 600 contributors, attracted 196,000 GitHub stars and sort-of been featured in an extremely vague Super Bowl commercial for AI.com.
Quoting AI.com founder Kris Marszalek, purchaser of the most expensive domain in history for $70m:
ai.com is the world’s first easy-to-use and secure implementation of OpenClaw, the open source agent framework that went viral two weeks ago; we made it easy to use without any technical skills, while hardening security to keep your data safe.
Looks like vaporware to me - all you can do right now is reserve a handle - but it's still remarkable to see an open source project get to that level of hype in such a short space of time.
Update: OpenClaw creator Peter Steinberger just announced that he's joining OpenAI and plans to transfer ownership of OpenClaw to a new independent foundation.
Gwtar: a static efficient single-file HTML format (via) Fascinating new project from Gwern Branwen and Said Achmiz that targets the challenge of combining large numbers of assets into a single archived HTML file without that file being inconvenient to view in a browser.
The key trick it uses is to fire window.stop() early in the page to prevent the browser from downloading the whole thing, then following that call with inline tar uncompressed content.
It can then make HTTP range requests to fetch content from that tar data on-demand when it is needed by the page.
The JavaScript that has already loaded rewrites asset URLs to point to https://localhost/ purely so that they will fail to load. Then it uses a PerformanceObserver to catch those attempted loads:
let perfObserver = new PerformanceObserver((entryList, observer) => {
resourceURLStringsHandler(entryList.getEntries().map(entry => entry.name));
});
perfObserver.observe({ entryTypes: [ "resource" ] });
That resourceURLStringsHandler callback finds the resource if it is already loaded or fetches it with an HTTP range request otherwise and then inserts the resource in the right place using a blob: URL.
Here's what the window.stop() portion of the document looks like if you view the source:
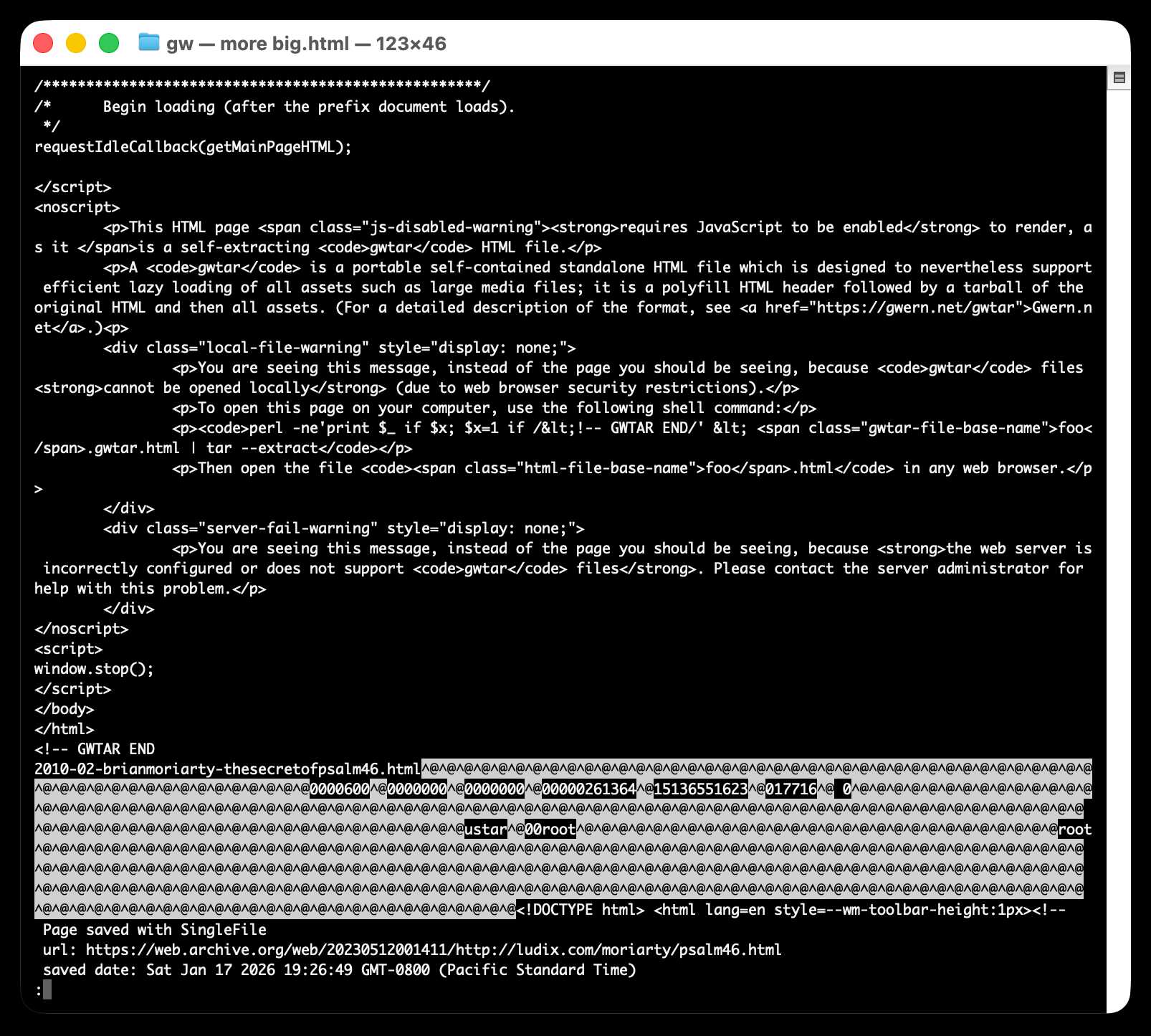
Amusingly for an archive format it doesn't actually work if you open the file directly on your own computer. Here's what you see if you try to do that:
You are seeing this message, instead of the page you should be seeing, because
gwtarfiles cannot be opened locally (due to web browser security restrictions).To open this page on your computer, use the following shell command:
perl -ne'print $_ if $x; $x=1 if /<!-- GWTAR END/' < foo.gwtar.html | tar --extractThen open the file
foo.htmlin any web browser.
Deep Blue
We coined a new term on the Oxide and Friends podcast last month (primary credit to Adam Leventhal) covering the sense of psychological ennui leading into existential dread that many software developers are feeling thanks to the encroachment of generative AI into their field of work.
[... 971 words]I'm occasionally accused of using LLMs to write the content on my blog. I don't do that, and I don't think my writing has much of an LLM smell to it... with one notable exception:
# Finally, do em dashes s = s.replace(' - ', u'\u2014')
That code to add em dashes to my posts dates back to at least 2015 when I ported my blog from an older version of Django (in a long-lost Mercurial repository) and started afresh on GitHub.
The AI Vampire (via) Steve Yegge's take on agent fatigue, and its relationship to burnout.
Let's pretend you're the only person at your company using AI.
In Scenario A, you decide you're going to impress your employer, and work for 8 hours a day at 10x productivity. You knock it out of the park and make everyone else look terrible by comparison.
In that scenario, your employer captures 100% of the value from you adopting AI. You get nothing, or at any rate, it ain't gonna be 9x your salary. And everyone hates you now.
And you're exhausted. You're tired, Boss. You got nothing for it.
Congrats, you were just drained by a company. I've been drained to the point of burnout several times in my career, even at Google once or twice. But now with AI, it's oh, so much easier.
Steve reports needing more sleep due to the cognitive burden involved in agentic engineering, and notes that four hours of agent work a day is a more realistic pace:
I’ve argued that AI has turned us all into Jeff Bezos, by automating the easy work, and leaving us with all the difficult decisions, summaries, and problem-solving. I find that I am only really comfortable working at that pace for short bursts of a few hours once or occasionally twice a day, even with lots of practice.
