157 posts tagged “postgresql”
2021
Weeknotes: Vaccinate The States, and how I learned that returning dozens of MB of JSON works just fine these days
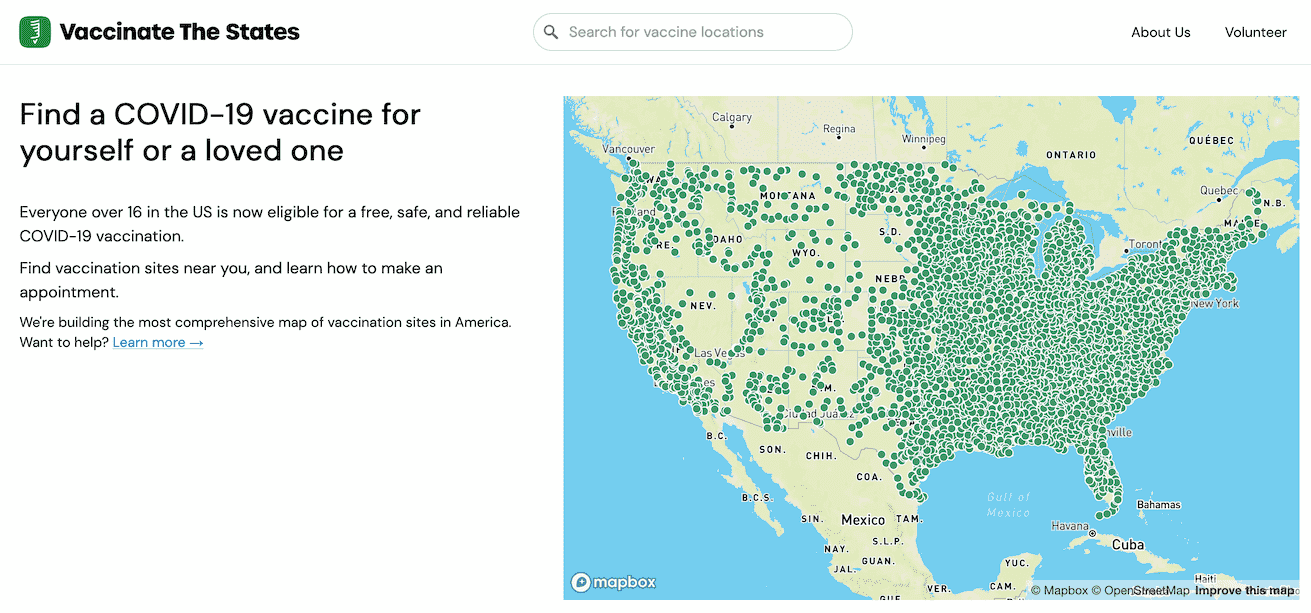
On Friday VaccinateCA grew in scope, a lot: we launched a new website called Vaccinate The States. Patrick McKenzie wrote more about the project here—the short version is that we’re building the most comprehensive possible dataset of vaccine availability in the USA, using a combination of data collation, online research and continuing to make a huge number of phone calls.
[... 1,109 words]Porting VaccinateCA to Django
As I mentioned back in February, I’ve been working with the VaccinateCA project to try to bring the pandemic to an end a little earlier by helping gather as accurate a model as possible of where the Covid vaccine is available in California and how people can get it.
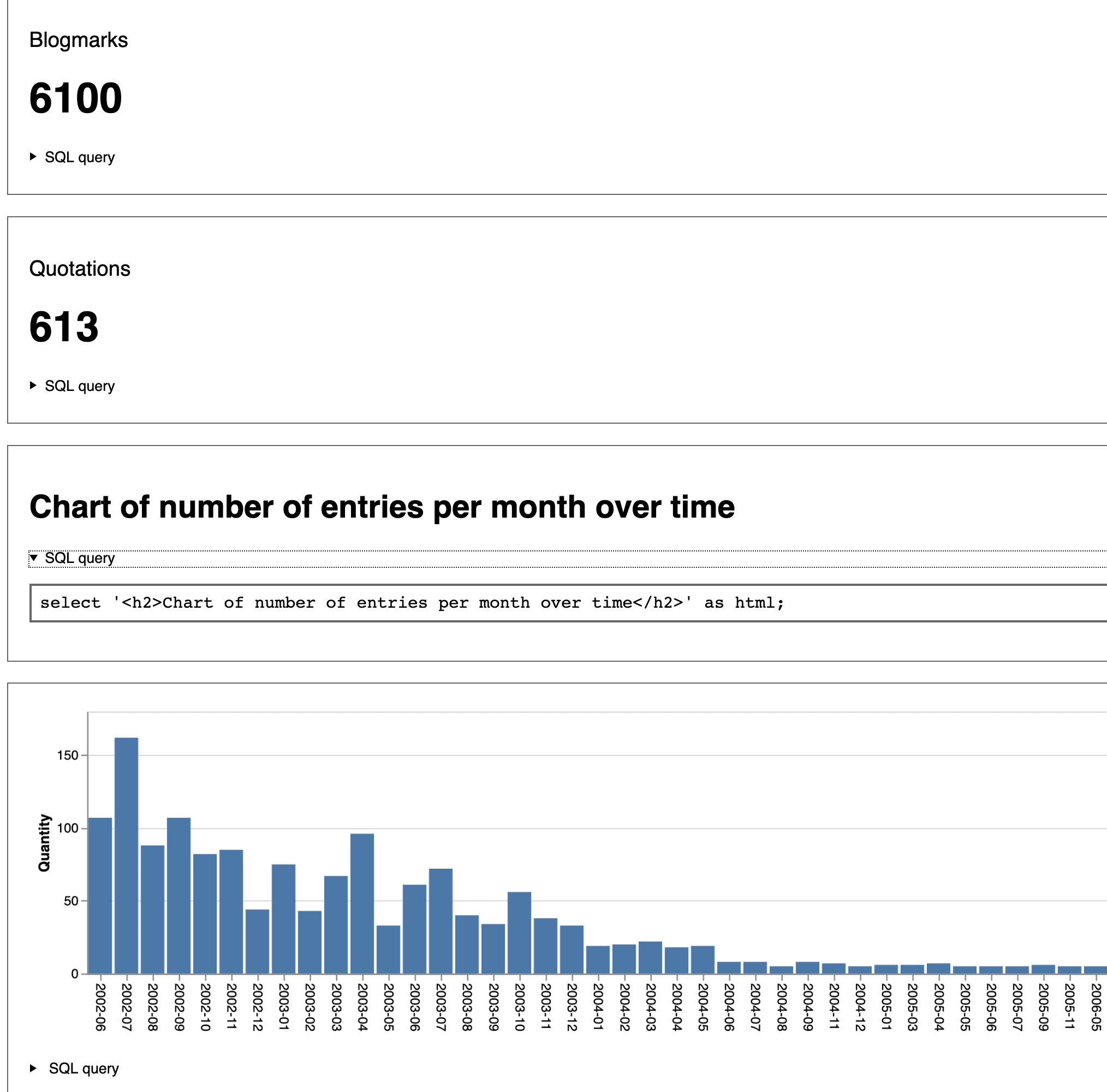
[... 2,157 words]Weeknotes: django-sql-dashboard widgets
A few small releases this week, for django-sql-dashboard, datasette-auth-passwords and datasette-publish-vercel.
VIAL is now live, plus django-sql-dashboard
Our new Django backend has now officially graduated from preview mode! We’ve been running it to collect caller reports for Oregon for over a week now, and today we finally turned off the old Heroku app and promoted https://vial.calltheshots.us/ to be the place that our caller app writes to.
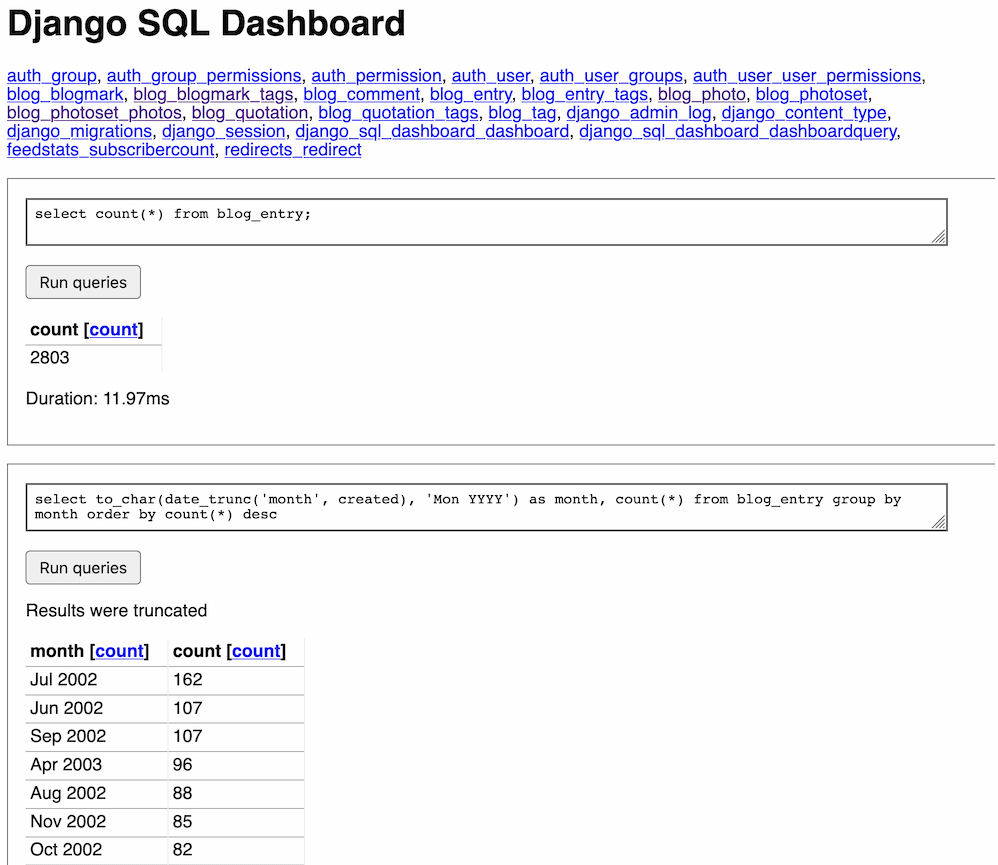
[... 672 words]Weeknotes: tableau-to-sqlite, django-sql-dashboard
This week I started a limited production run of my new backend for Vaccinate CA calling, built a tableau-to-sqlite import tool and started working on a subset of Datasette for PostgreSQL and Django called django-sql-dashboard.
Trying to end the pandemic a little earlier with VaccinateCA
This week I got involved with the VaccinateCA effort. We are trying to end the pandemic a little earlier, by building the most accurate database possible of vaccination locations and availability in California.
[... 1,154 words]Django admin customization, JSON in our PostgreSQL
My progress slowed a bit today as I started digging into some things I’m less familiar with—but I’ve found some tricks that I think will help us out a lot.
[... 1,089 words]Spinning up a new Django app to act as a backend for VaccinateCA
My goal by the end of this week is to have a working proof of concept for a Django + PostgreSQL app that can replace Airtable as the principle backend for the https://www.vaccinateca.com/ site. This proof of concept will allow us to make a go or no-go decision and figure out what else needs to be implemented before we can start using it to track calls.
[... 762 words]Fuzzy Name Matching in Postgres. Paul Ramsey describes how to implement fuzzy name matching in PostgreSQL using the fuzzystrmatch extension and its levenshtein() and soundex() functions, plus functional indexes to query against indexed soundex first and then apply slower Levenshtein. The same tricks should also work against SQLite using the datasette-jellyfish plugin.
Cleaning Up Your Postgres Database (via) Craig Kerstiens provides some invaluable tips on running an initial check of the health of a PostgreSQL database, by using queries against the pg_statio_user_indexes table to find the memory cache hit ratio and the pg_stat_user_tables table to see what percentage of queries to your tables are using an index.
2020
DuckDB (via) This is a really interesting, relatively new database. It’s kind of a weird hybrid between SQLite and PostgreSQL: it uses the PostgreSQL parser but models itself after SQLite in that databases are a single file and the code is designed for use as an embedded library, distributed in a single amalgamation C++ file (SQLite uses a C amalgamation). It features a “columnar-vectorized query execution engine” inspired by MonetDB (also by the DuckDB authors) and is hence designed to run analytical queries really quickly. You can install it using “pip install duckdb”—the resulting module feels similar to Python’s sqlite3, and follows roughly the same DBAPI pattern.
Some SQL Tricks of an Application DBA (via) This post taught me so many PostgreSQL tricks that I hadn’t seen before. Did you know you can start a transaction, drop an index, run explain and then rollback the transaction (cancelling the index drop) to see what explain would look like without that index? Among other things I also learned what the “correlation” database statistic does: it’s a measure of how close-to-sorted the values in a specific column are, which helps PostgreSQL decide if it should do an index scan or a bitmap scan when making use of an index.
PostgreSQL full-text search in the Django Admin. Today I figured out how to use PostgreSQL full-text search in the Django admin for my blog, using the get_search_results method on a subclass of ModelAdmin.
Get Started—Materialize. Materialize is a really interesting new database—“a streaming SQL materialized view engine”. It builds materialized views on top of streaming data sources (such as Kafka)—you define the view using a SQL query, then it figures out how to keep that view up-to-date automatically as new data streams in. It speaks the PostgreSQL protocol so you can talk to it using the psql tool or any PostgreSQL client library. The “get started” guide is particularly impressive: it uses a curl stream of the Wikipedia recent changes API, parsed using a regular expression. And it’s written in Rust, so installing it is as easy as downloading and executing a single binary (though I used Homebrew).
PostGraphile: Production Considerations. PostGraphile is a tool for building a GraphQL API on top of an existing PostgreSQL schema. Their “production considerations” documentation is particularly interesting because it directly addresses some of my biggest worries about GraphQL: the potential for someone to craft an expensive query that ties up server resources. PostGraphile suggests a number of techniques for avoiding this, including a statement timeout, a query allowlist, pagination caps and (in their “pro” version) a cost limit that uses a calculated cost score for the query.
Generated Columns in SQLite (via) SQLite 3.31.0 released today, and generated columns are the single most notable new feature. PostgreSQL 12 added these in October 2019, and MySQL has had them since 5.7 in October 2015. MySQL and SQLite both offer either “stored” or “virtual” generated columns, with virtual columns being calculated at runtime. PostgreSQL currently only supports stored columns.
2019
db-to-sqlite 1.0 release. I’ve released version 1.0 of my db-to-sqlite tool, which lets you create a SQLite database copy of any database supported by SQLAlchemy (I’ve tested it against MySQL and PostgreSQL). The tool has a bunch of new features: you can use --redact to redact specific columns, specify --table multiple times to copy a subset of tables, and the --all option now efficiently adds all foreign keys at the end of the import. The project now has unit tests which run against MySQL and PostgreSQL in Travis CI. Also included in the README: a shell one-liner for creating a local SQLite copy of a remote Heroku Postgres database based on extracting the connection string from a Heroku config environment variable.
How to Create an Index in Django Without Downtime (via) Excellent advanced tutorial on Django migrations, which uses a desire to create indexes in PostgreSQL without locking the table (with CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY) to explain the SeparateDatabaseAndState and atomic features of Django’s migration framework.
zson (via) “ZSON is a PostgreSQL extension for transparent JSONB compression. Compression is based on a shared dictionary of strings most frequently used in specific JSONB documents [...] In some cases ZSON can save half of your disk space and give you about 10% more TPS.”
django-zombodb (via) The hardest part of working with an external search engine like Elasticsearch is always keeping that index synchronized with your relational database. ZomboDB is a PostgreSQL extension which lets you create a new type of index backed by an external Elasticsearch cluster. Updated rows will be pushed to the index automatically, and custom SQL syntax can then be used to execute searches. django-zombodb is a brand new library by Flávio Juvenal which integrates ZomboDB directly into the Django ORM, letting you add Elasticsearch-backed functionality with just a few lines of extra configuration. It even includes custom Django migrations for enabling the extension in PostgreSQL!
2018
Optimizing Django Admin Paginator. The Django admin paginator uses a count(*) to calculate the total number of rows, so it knows how many pages to display. This makes it unpleasantly slow over large datasets. Haki Benita has an ingenious solution: drop in a custom paginator which uses the PostgreSQL “SET LOCAL statement_timeout TO 200” statement first, then if a timeout error is raised returns 9999999999 as the count instead. This means small tables get accurate page counts and giant tables load display in the admin within a reasonable time period.
Experiences with running PostgreSQL on Kubernetes (via) Fascinating interview that makes a solid argument for the idea that running stateful data stores like PostgreSQL or Cassandra is made harder, not easier when you add an orchestration tool like Kubernetes into the mix.
mycli. Really neat auto-complete enabled MySQL terminal client, built using the excellent python-prompt-toolkit. Has a sister-project for PostgreSQL called pgcli.
Showdown: MySQL 8 vs PostgreSQL 10 (via) MySQL 8 makes comparisons between PostgreSQL and MySQL far more interesting, as it closes some of the key feature gaps. Meanwhile the PostgreSQL replication story (long one of MySQL’s key advantages) has improved dramatically in recent versions. This article offers a useful overview of the current differences, including diving into some of the less obvious implementation details that differ between the two.
Touring a Fast, Safe, and Complete(ish) Web Service in Rust. Brandur’s notes from building a high performance web service in Rust, using PostgreSQL via the Diesel ORM and the Rust actix-web framework which provides Erlang-style actors and promise-based async concurrency.
User-defined Order in SQL (via) This is a fun intellectual exercise: how can one efficiently implement a user-defined order in a SQL table? The obvious initial approach is to have an integer position column, but this means every subsequent row must be updated when an item changes position. Joe “begriffs” Nelson explores some clever alternatives, including floating point or decimal positions (allowing new items to be inserted at a midpoint between existing positions) and a new custom rational number type he buiIt as a PostgreSQL extension.
Conditional aggregation in Django 2.0 (via) I hadn’t realised how clever this new Django ORM feature by Tom Forbes is. It lets you build an aggregation against a subset of rows, e.g. Client.objects.aggregate(regular=Count(’pk’, filter=Q(account_type=Client.REGULAR)))—then if you are using PostgreSQL it translates it into a fast FILTER WHERE clause, while other databases emulate the same behaviour using a CASE statement.
How the Citus distributed database rebalances your data. Citus is a fascinating implementation of database sharding built on top of PostgreSQL primitives. PostgreSQL 10 introduced extremely flexible logical replication—in this post Craig Kerstiens explains how Citus use this new ability to re-balance shards (e.g. when you move from two to four physical PostgreSQL nodes) without downtime.
django-postgres-copy (via) Really neat Django queryset add-on which exposes the PostgreSQL COPY statement for importing (and exporting) CSV data. MyModel.objects.from_csv(“filename.csv”). Built by the team of data journalists at the California Civic Data Coalition.
2017
PostgreSQL Exercises. Excellent set of PostgreSQL exercises by Alisdair Owens, each with an interactive editor that lets you run your queries against a real database. Starts with the basics, but also covers advanced topics like recursive queries and window aggregate functions.