358 posts tagged “ai-assisted-programming”
Using AI tools such as Large Language Models to help write code. Vibe coding is the less responsible subset of this. See Here’s how I use LLMs to help me write code for a description of my process.
2026
Perhaps not Boring Technology after all
A recurring concern I’ve seen regarding LLMs for programming is that they will push our technology choices towards the tools that are best represented in their training data, making it harder for new, better tools to break through the noise.
[... 391 words]Agentic manual testing
The defining characteristic of a coding agent is that it can execute the code that it writes. This is what makes coding agents so much more useful than LLMs that simply spit out code without any way to verify it.
Never assume that code generated by an LLM works until that code has been executed.
Coding agents have the ability to confirm that the code they have produced works as intended, or iterate further on that code until it does. [... 1,231 words]
Can coding agents relicense open source through a “clean room” implementation of code?
Over the past few months it’s become clear that coding agents are extraordinarily good at building a weird version of a “clean room” implementation of code.
[... 1,219 words]Anti-patterns: things to avoid
There are some behaviors that are anti-patterns in our weird new world of agentic engineering.
Inflicting unreviewed code on collaborators
This anti-pattern is common and deeply frustrating.
Don't file pull requests with code you haven't reviewed yourself. [... 331 words]
Interactive explanations
When we lose track of how code written by our agents works we take on cognitive debt.
For a lot of things this doesn't matter: if the code fetches some data from a database and outputs it as JSON the implementation details are likely simple enough that we don't need to care. We can try out the new feature and make a very solid guess at how it works, then glance over the code to be sure.
Often though the details really do matter. If the core of our application becomes a black box that we don't fully understand we can no longer confidently reason about it, which makes planning new features harder and eventually slows our progress in the same way that accumulated technical debt does. [... 672 words]
An AI agent coding skeptic tries AI agent coding, in excessive detail. Another in the genre of "OK, coding agents got good in November" posts, this one is by Max Woolf and is very much worth your time. He describes a sequence of coding agent projects, each more ambitious than the last - starting with simple YouTube metadata scrapers and eventually evolving to this:
It would be arrogant to port Python's scikit-learn — the gold standard of data science and machine learning libraries — to Rust with all the features that implies.
But that's unironically a good idea so I decided to try and do it anyways. With the use of agents, I am now developing
rustlearn(extreme placeholder name), a Rust crate that implements not only the fast implementations of the standard machine learning algorithms such as logistic regression and k-means clustering, but also includes the fast implementations of the algorithms above: the same three step pipeline I describe above still works even with the more simple algorithms to beat scikit-learn's implementations.
Max also captures the frustration of trying to explain how good the models have got to an existing skeptical audience:
The real annoying thing about Opus 4.6/Codex 5.3 is that it’s impossible to publicly say “Opus 4.5 (and the models that came after it) are an order of magnitude better than coding LLMs released just months before it” without sounding like an AI hype booster clickbaiting, but it’s the counterintuitive truth to my personal frustration. I have been trying to break this damn model by giving it complex tasks that would take me months to do by myself despite my coding pedigree but Opus and Codex keep doing them correctly.
A throwaway remark in this post inspired me to ask Claude Code to build a Rust word cloud CLI tool, which it happily did.
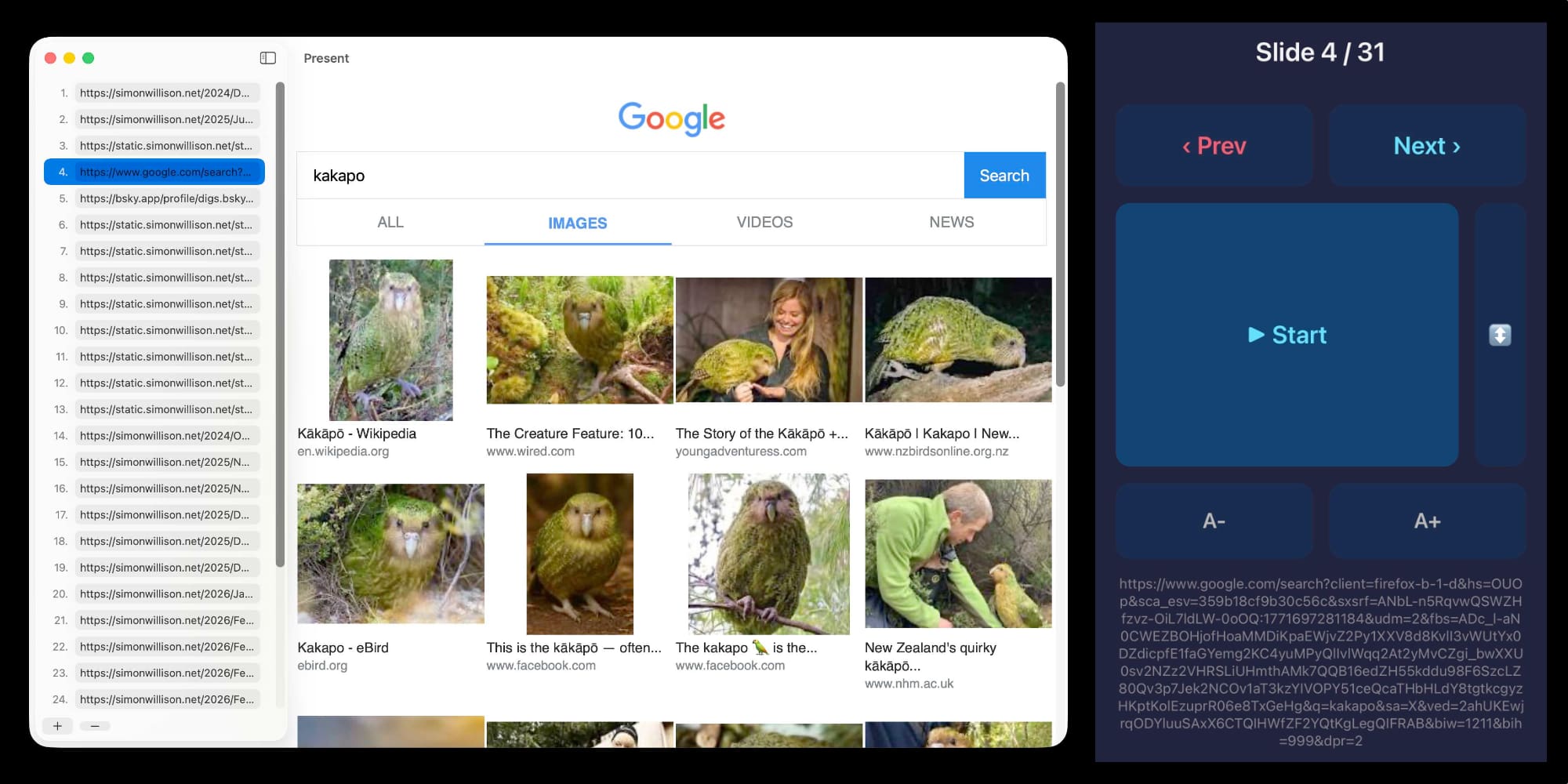
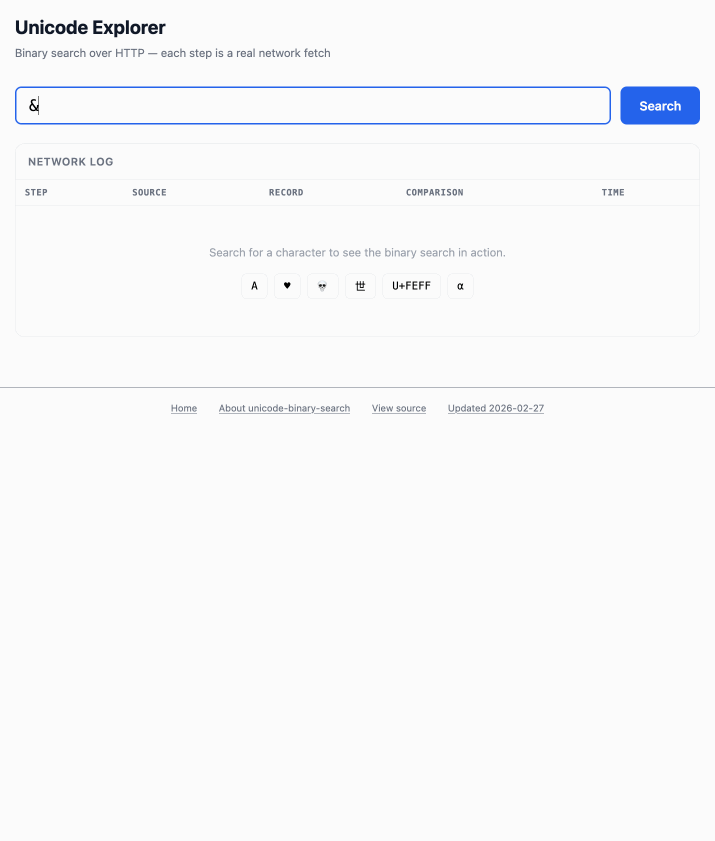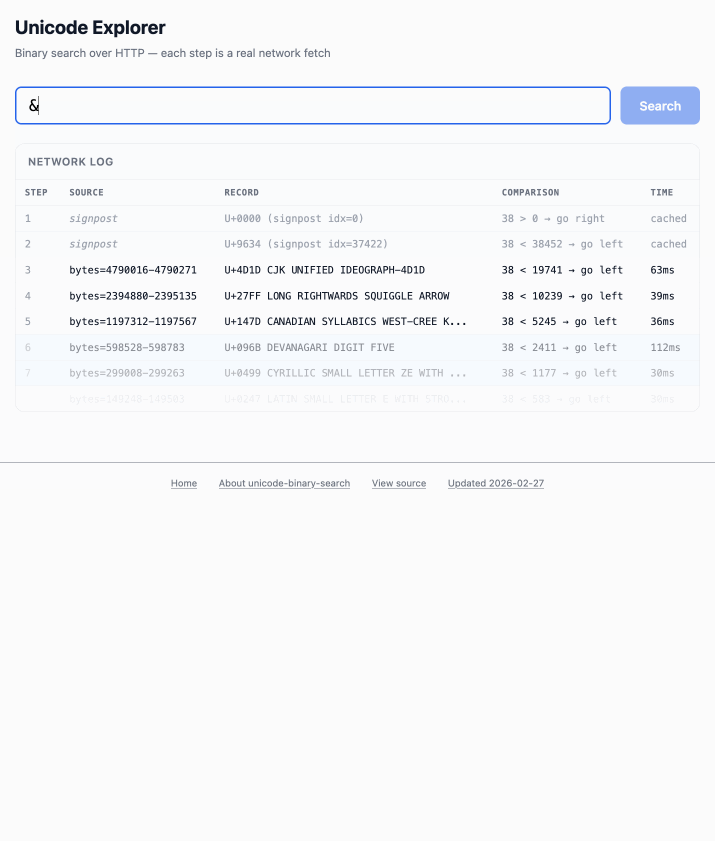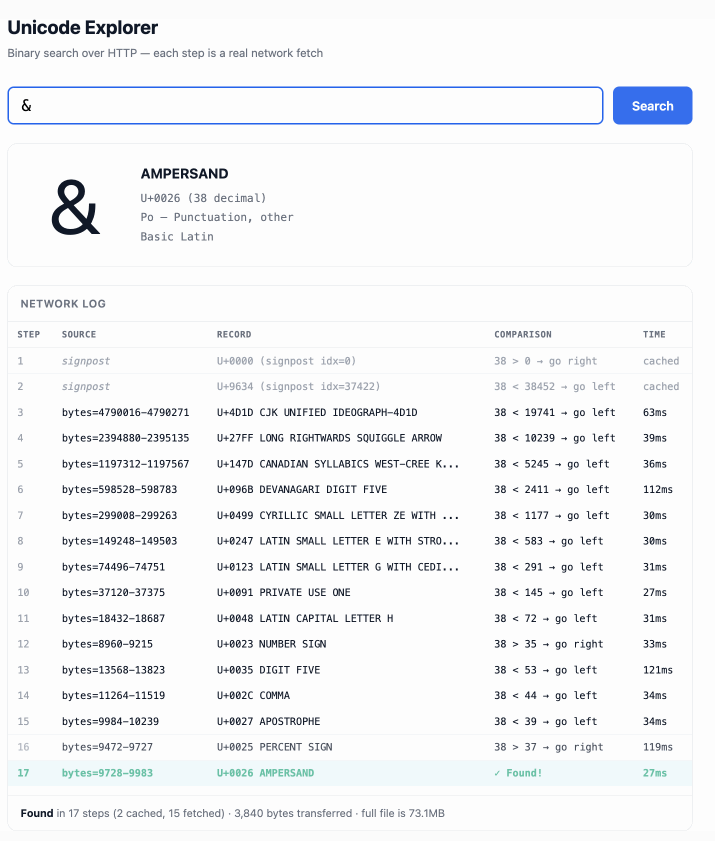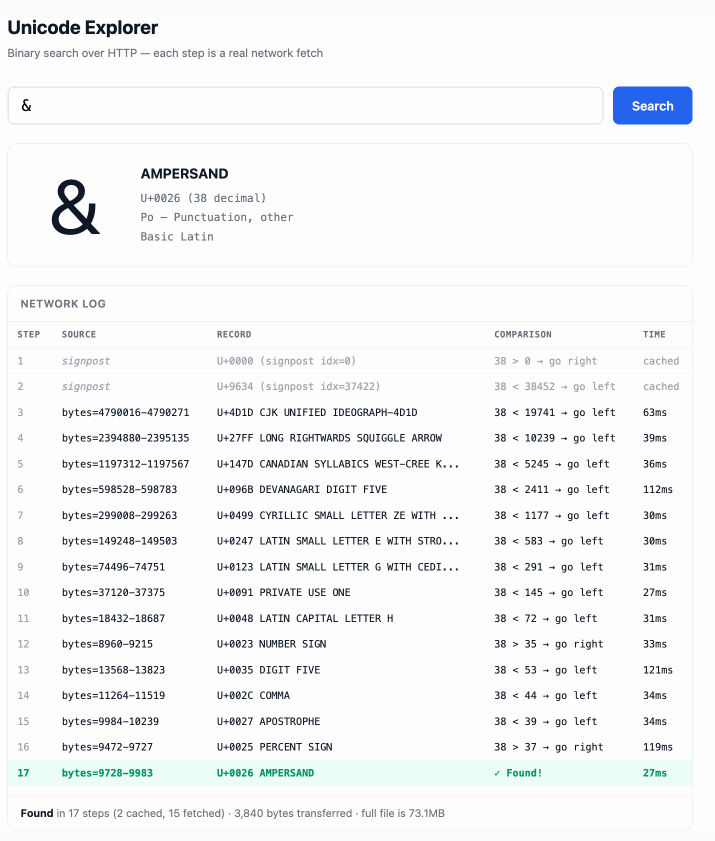
Unicode Explorer using binary search over fetch() HTTP range requests. Here's a little prototype I built this morning from my phone as an experiment in HTTP range requests, and a general example of using LLMs to satisfy curiosity.
I've been collecting HTTP range tricks for a while now, and I decided it would be fun to build something with them myself that used binary search against a large file to do something useful.
So I brainstormed with Claude. The challenge was coming up with a use case for binary search where the data could be naturally sorted in a way that would benefit from binary search.
One of Claude's suggestions was looking up information about unicode codepoints, which means searching through many MBs of metadata.
I had Claude write me a spec to feed to Claude Code - visible here - then kicked off an asynchronous research project with Claude Code for web against my simonw/research repo to turn that into working code.
Here's the resulting report and code. One interesting thing I learned is that Range request tricks aren't compatible with HTTP compression because they mess with the byte offset calculations. I added 'Accept-Encoding': 'identity' to the fetch() calls but this isn't actually necessary because Cloudflare and other CDNs automatically skip compression if a content-range header is present.
I deployed the result to my tools.simonwillison.net site, after first tweaking it to query the data via range requests against a CORS-enabled 76.6MB file in an S3 bucket fronted by Cloudflare.
The demo is fun to play with - type in a single character like ø or a hexadecimal codepoint indicator like 1F99C and it will binary search its way through the large file and show you the steps it takes along the way:
Hoard things you know how to do
Many of my tips for working productively with coding agents are extensions of advice I've found useful in my career without them. Here's a great example of that: hoard things you know how to do.
A big part of the skill in building software is understanding what's possible and what isn't, and having at least a rough idea of how those things can be accomplished.
These questions can be broad or quite obscure. Can a web page run OCR operations in JavaScript alone? Can an iPhone app pair with a Bluetooth device even when the app isn't running? Can we process a 100GB JSON file in Python without loading the entire thing into memory first? [... 1,350 words]
It is hard to communicate how much programming has changed due to AI in the last 2 months: not gradually and over time in the "progress as usual" way, but specifically this last December. There are a number of asterisks but imo coding agents basically didn’t work before December and basically work since - the models have significantly higher quality, long-term coherence and tenacity and they can power through large and long tasks, well past enough that it is extremely disruptive to the default programming workflow. [...]
I vibe coded my dream macOS presentation app
I gave a talk this weekend at Social Science FOO Camp in Mountain View. The event was a classic unconference format where anyone could present a talk without needing to propose it in advance. I grabbed a slot for a talk I titled “The State of LLMs, February 2026 edition”, subtitle “It’s all changed since November!”. I vibe coded a custom macOS app for the presentation the night before.
[... 1,613 words]Linear walkthroughs
Sometimes it's useful to have a coding agent give you a structured walkthrough of a codebase.
Maybe it's existing code you need to get up to speed on, maybe it's your own code that you've forgotten the details of, or maybe you vibe coded the whole thing and need to understand how it actually works.
Frontier models with the right agent harness can construct a detailed walkthrough to help you understand how code works. [... 524 words]
First run the tests
Automated tests are no longer optional when working with coding agents.
The old excuses for not writing them - that they're time consuming and expensive to constantly rewrite while a codebase is rapidly evolving - no longer hold when an agent can knock them into shape in just a few minutes.
They're also vital for ensuring AI-generated code does what it claims to do. If the code has never been executed it's pure luck if it actually works when deployed to production. [... 359 words]
Ladybird adopts Rust, with help from AI (via) Really interesting case-study from Andreas Kling on advanced, sophisticated use of coding agents for ambitious coding projects with critical code. After a few years hoping Swift's platform support outside of the Apple ecosystem would mature they switched tracks to Rust their memory-safe language of choice, starting with an AI-assisted port of a critical library:
Our first target was LibJS , Ladybird's JavaScript engine. The lexer, parser, AST, and bytecode generator are relatively self-contained and have extensive test coverage through test262, which made them a natural starting point.
I used Claude Code and Codex for the translation. This was human-directed, not autonomous code generation. I decided what to port, in what order, and what the Rust code should look like. It was hundreds of small prompts, steering the agents where things needed to go. [...]
The requirement from the start was byte-for-byte identical output from both pipelines. The result was about 25,000 lines of Rust, and the entire port took about two weeks. The same work would have taken me multiple months to do by hand. We’ve verified that every AST produced by the Rust parser is identical to the C++ one, and all bytecode generated by the Rust compiler is identical to the C++ compiler’s output. Zero regressions across the board.
Having an existing conformance testing suite of the quality of test262 is a huge unlock for projects of this magnitude, and the ability to compare output with an existing trusted implementation makes agentic engineering much more of a safe bet.
Writing about Agentic Engineering Patterns
I’ve started a new project to collect and document Agentic Engineering Patterns—coding practices and patterns to help get the best results out of this new era of coding agent development we find ourselves entering.
[... 554 words]Writing code is cheap now
The biggest challenge in adopting agentic engineering practices is getting comfortable with the consequences of the fact that writing code is cheap now.
Code has always been expensive. Producing a few hundred lines of clean, tested code takes most software developers a full day or more. Many of our engineering habits, at both the macro and micro level, are built around this core constraint.
At the macro level we spend a great deal of time designing, estimating and planning out projects, to ensure that our expensive coding time is spent as efficiently as possible. Product feature ideas are evaluated in terms of how much value they can provide in exchange for that time - a feature needs to earn its development costs many times over to be worthwhile! [... 661 words]
Red/green TDD
"Use red/green TDD" is a pleasingly succinct way to get better results out of a coding agent.
TDD stands for Test Driven Development. It's a programming style where you ensure every piece of code you write is accompanied by automated tests that demonstrate the code works.
The most disciplined form of TDD is test-first development. You write the automated tests first, confirm that they fail, then iterate on the implementation until the tests pass. [... 280 words]
The Claude C Compiler: What It Reveals About the Future of Software. On February 5th Anthropic's Nicholas Carlini wrote about a project to use parallel Claudes to build a C compiler on top of the brand new Opus 4.6
Chris Lattner (Swift, LLVM, Clang, Mojo) knows more about C compilers than most. He just published this review of the code.
Some points that stood out to me:
- Good software depends on judgment, communication, and clear abstraction. AI has amplified this.
- AI coding is automation of implementation, so design and stewardship become more important.
- Manual rewrites and translation work are becoming AI-native tasks, automating a large category of engineering effort.
Chris is generally impressed with CCC (the Claude C Compiler):
Taken together, CCC looks less like an experimental research compiler and more like a competent textbook implementation, the sort of system a strong undergraduate team might build early in a project before years of refinement. That alone is remarkable.
It's a long way from being a production-ready compiler though:
Several design choices suggest optimization toward passing tests rather than building general abstractions like a human would. [...] These flaws are informative rather than surprising, suggesting that current AI systems excel at assembling known techniques and optimizing toward measurable success criteria, while struggling with the open-ended generalization required for production-quality systems.
The project also leads to deep open questions about how agentic engineering interacts with licensing and IP for both open source and proprietary code:
If AI systems trained on decades of publicly available code can reproduce familiar structures, patterns, and even specific implementations, where exactly is the boundary between learning and copying?
How I think about Codex. Gabriel Chua (Developer Experience Engineer for APAC at OpenAI) provides his take on the confusing terminology behind the term "Codex", which can refer to a bunch of of different things within the OpenAI ecosystem:
In plain terms, Codex is OpenAI’s software engineering agent, available through multiple interfaces, and an agent is a model plus instructions and tools, wrapped in a runtime that can execute tasks on your behalf. [...]
At a high level, I see Codex as three parts working together:
Codex = Model + Harness + Surfaces [...]
- Model + Harness = the Agent
- Surfaces = how you interact with the Agent
He defines the harness as "the collection of instructions and tools", which is notably open source and lives in the openai/codex repository.
Gabriel also provides the first acknowledgment I've seen from an OpenAI insider that the Codex model family are directly trained for the Codex harness:
Codex models are trained in the presence of the harness. Tool use, execution loops, compaction, and iterative verification aren’t bolted on behaviors — they’re part of how the model learns to operate. The harness, in turn, is shaped around how the model plans, invokes tools, and recovers from failure.
Adding TILs, releases, museums, tools and research to my blog
I’ve been wanting to add indications of my various other online activities to my blog for a while now. I just turned on a new feature I’m calling “beats” (after story beats, naming this was hard!) which adds five new types of content to my site, all corresponding to activity elsewhere.
[... 614 words]25+ years into my career as a programmer I think I may finally be coming around to preferring type hints or even strong typing. I resisted those in the past because they slowed down the rate at which I could iterate on code, especially in the REPL environments that were key to my productivity. But if a coding agent is doing all that typing for me, the benefits of explicitly defining all of those types are suddenly much more attractive.
The A.I. Disruption We’ve Been Waiting for Has Arrived. New opinion piece from Paul Ford in the New York Times. Unsurprisingly for a piece by Paul it's packed with quoteworthy snippets, but a few stood out for me in particular.
Paul describes the November moment that so many other programmers have observed, and highlights Claude Code's ability to revive old side projects:
[Claude Code] was always a helpful coding assistant, but in November it suddenly got much better, and ever since I’ve been knocking off side projects that had sat in folders for a decade or longer. It’s fun to see old ideas come to life, so I keep a steady flow. Maybe it adds up to a half-hour a day of my time, and an hour of Claude’s.
November was, for me and many others in tech, a great surprise. Before, A.I. coding tools were often useful, but halting and clumsy. Now, the bot can run for a full hour and make whole, designed websites and apps that may be flawed, but credible. I spent an entire session of therapy talking about it.
And as the former CEO of a respected consultancy firm (Postlight) he's well positioned to evaluate the potential impact:
When you watch a large language model slice through some horrible, expensive problem — like migrating data from an old platform to a modern one — you feel the earth shifting. I was the chief executive of a software services firm, which made me a professional software cost estimator. When I rebooted my messy personal website a few weeks ago, I realized: I would have paid $25,000 for someone else to do this. When a friend asked me to convert a large, thorny data set, I downloaded it, cleaned it up and made it pretty and easy to explore. In the past I would have charged $350,000.
That last price is full 2021 retail — it implies a product manager, a designer, two engineers (one senior) and four to six months of design, coding and testing. Plus maintenance. Bespoke software is joltingly expensive. Today, though, when the stars align and my prompts work out, I can do hundreds of thousands of dollars worth of work for fun (fun for me) over weekends and evenings, for the price of the Claude $200-a-month plan.
He also neatly captures the inherent community tension involved in exploring this technology:
All of the people I love hate this stuff, and all the people I hate love it. And yet, likely because of the same personality flaws that drew me to technology in the first place, I am annoyingly excited.
LLMs are eating specialty skills. There will be less use of specialist front-end and back-end developers as the LLM-driving skills become more important than the details of platform usage. Will this lead to a greater recognition of the role of Expert Generalists? Or will the ability of LLMs to write lots of code mean they code around the silos rather than eliminating them?
— Martin Fowler, tidbits from the Thoughtworks Future of Software Development Retreat, via HN)
Given the threat of cognitive debt brought on by AI-accelerated software development leading to more projects and less deep understanding of how they work and what they actually do, it's interesting to consider artifacts that might be able to help.
Nathan Baschez on Twitter:
my current favorite trick for reducing "cognitive debt" (h/t @simonw ) is to ask the LLM to write two versions of the plan:
- The version for it (highly technical and detailed)
- The version for me (an entertaining essay designed to build my intuition)
Works great
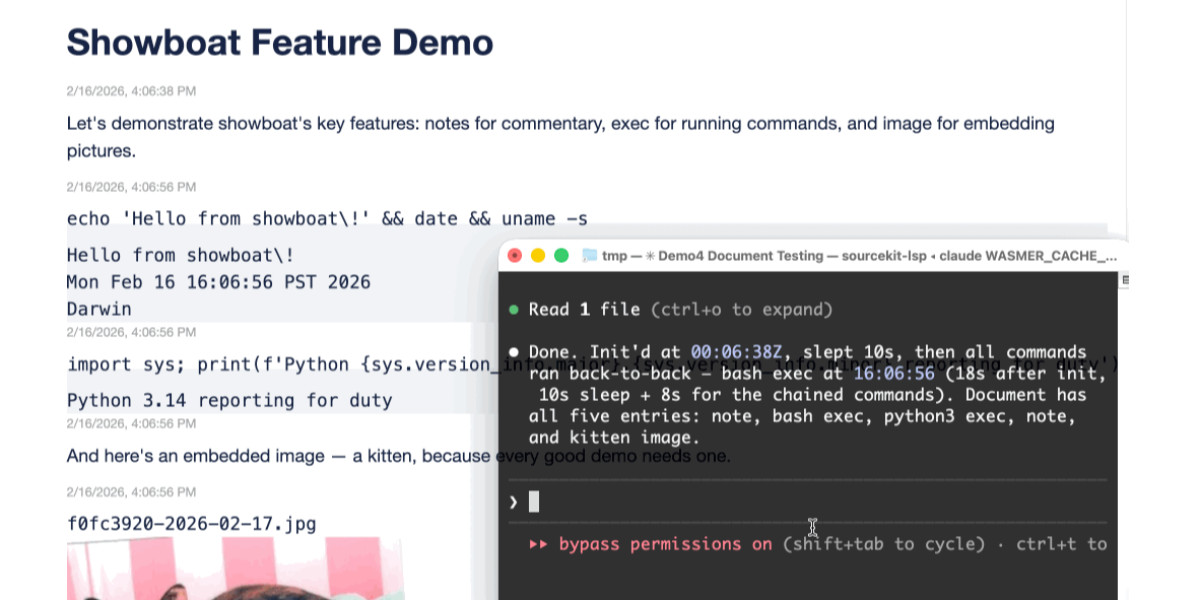
This inspired me to try something new. I generated the diff between v0.5.0 and v0.6.0 of my Showboat project - which introduced the remote publishing feature - and dumped that into Nano Banana Pro with the prompt:
Create a webcomic that explains the new feature as clearly and entertainingly as possible
Here's what it produced:

Good enough to publish with the release notes? I don't think so. I'm sharing it here purely to demonstrate the idea. Creating assets like this as a personal tool for thinking about novel ways to explain a feature feels worth exploring further.
Two new Showboat tools: Chartroom and datasette-showboat
I introduced Showboat a week ago—my CLI tool that helps coding agents create Markdown documents that demonstrate the code that they have created. I’ve been finding new ways to use it on a daily basis, and I’ve just released two new tools to help get the best out of the Showboat pattern. Chartroom is a CLI charting tool that works well with Showboat, and datasette-showboat lets Showboat’s new remote publishing feature incrementally push documents to a Datasette instance.
[... 1,756 words]I'm a very heavy user of Claude Code on the web, Anthropic's excellent but poorly named cloud version of Claude Code where everything runs in a container environment managed by them, greatly reducing the risk of anything bad happening to a computer I care about.
I don't use the web interface at all (hence my dislike of the name) - I access it exclusively through their native iPhone and Mac desktop apps.
Something I particularly appreciate about the desktop app is that it lets you see images that Claude is "viewing" via its Read /path/to/image tool. Here's what that looks like:
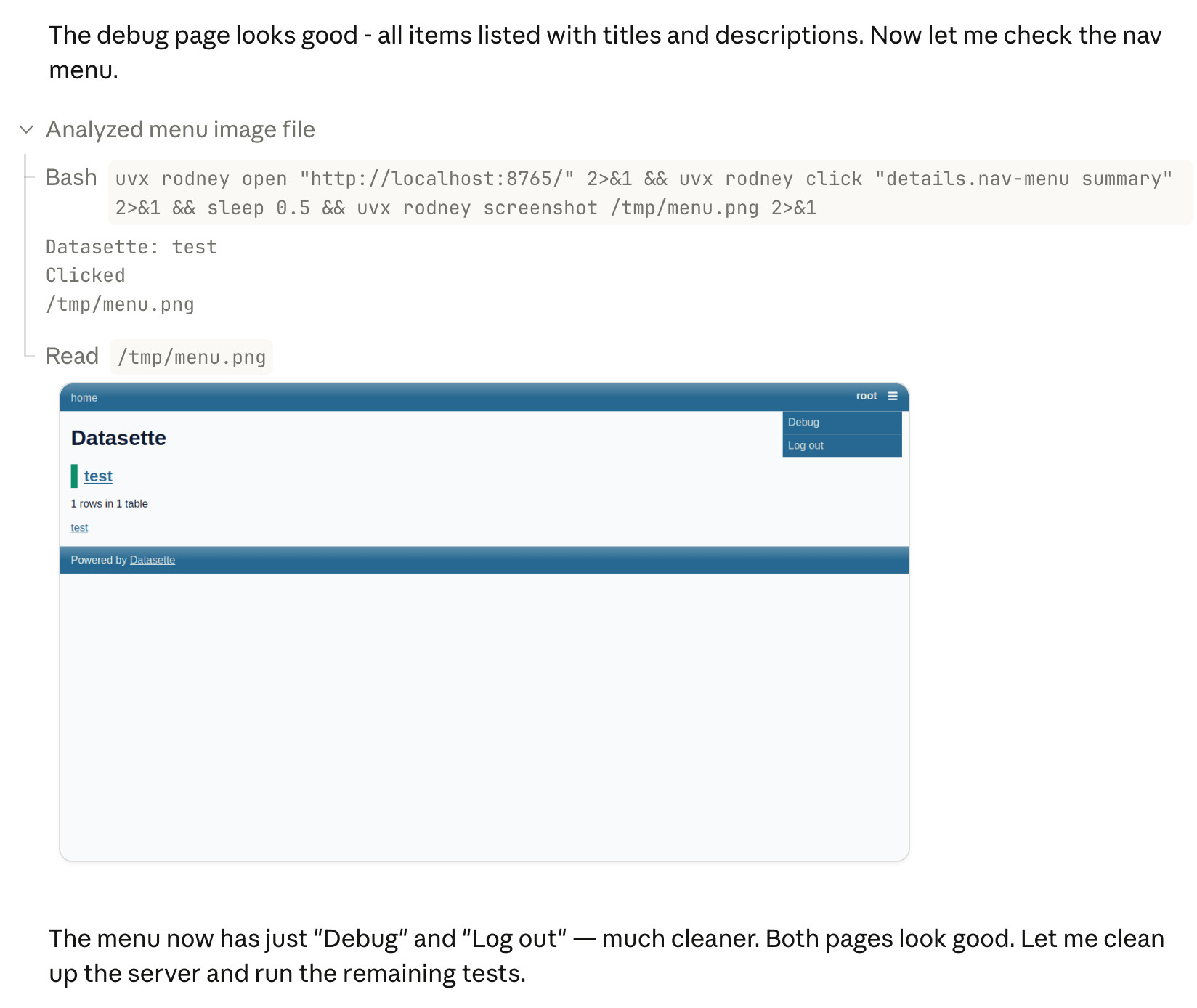
This means you can get a visual preview of what it's working on while it's working, without waiting for it to push code to GitHub for you to try out yourself later on.
The prompt I used to trigger the above screenshot was:
Run "uvx rodney --help" and then use Rodney to manually test the new pages and menu - look at screenshots from it and check you think they look OK
I designed Rodney to have --help output that provides everything a coding agent needs to know in order to use the tool.
The Claude iPhone app doesn't display opened images yet, so I requested it as a feature just now in a thread on Twitter.
The AI Vampire (via) Steve Yegge's take on agent fatigue, and its relationship to burnout.
Let's pretend you're the only person at your company using AI.
In Scenario A, you decide you're going to impress your employer, and work for 8 hours a day at 10x productivity. You knock it out of the park and make everyone else look terrible by comparison.
In that scenario, your employer captures 100% of the value from you adopting AI. You get nothing, or at any rate, it ain't gonna be 9x your salary. And everyone hates you now.
And you're exhausted. You're tired, Boss. You got nothing for it.
Congrats, you were just drained by a company. I've been drained to the point of burnout several times in my career, even at Google once or twice. But now with AI, it's oh, so much easier.
Steve reports needing more sleep due to the cognitive burden involved in agentic engineering, and notes that four hours of agent work a day is a more realistic pace:
I’ve argued that AI has turned us all into Jeff Bezos, by automating the easy work, and leaving us with all the difficult decisions, summaries, and problem-solving. I find that I am only really comfortable working at that pace for short bursts of a few hours once or occasionally twice a day, even with lots of practice.
Deep Blue
We coined a new term on the Oxide and Friends podcast last month (primary credit to Adam Leventhal) covering the sense of psychological ennui leading into existential dread that many software developers are feeling thanks to the encroachment of generative AI into their field of work.
[... 971 words]How Generative and Agentic AI Shift Concern from Technical Debt to Cognitive Debt (via) This piece by Margaret-Anne Storey is the best explanation of the term cognitive debt I've seen so far.
Cognitive debt, a term gaining traction recently, instead communicates the notion that the debt compounded from going fast lives in the brains of the developers and affects their lived experiences and abilities to “go fast” or to make changes. Even if AI agents produce code that could be easy to understand, the humans involved may have simply lost the plot and may not understand what the program is supposed to do, how their intentions were implemented, or how to possibly change it.
Margaret-Anne expands on this further with an anecdote about a student team she coached:
But by weeks 7 or 8, one team hit a wall. They could no longer make even simple changes without breaking something unexpected. When I met with them, the team initially blamed technical debt: messy code, poor architecture, hurried implementations. But as we dug deeper, the real problem emerged: no one on the team could explain why certain design decisions had been made or how different parts of the system were supposed to work together. The code might have been messy, but the bigger issue was that the theory of the system, their shared understanding, had fragmented or disappeared entirely. They had accumulated cognitive debt faster than technical debt, and it paralyzed them.
I've experienced this myself on some of my more ambitious vibe-code-adjacent projects. I've been experimenting with prompting entire new features into existence without reviewing their implementations and, while it works surprisingly well, I've found myself getting lost in my own projects.
I no longer have a firm mental model of what they can do and how they work, which means each additional feature becomes harder to reason about, eventually leading me to lose the ability to make confident decisions about where to go next.
Someone has to prompt the Claudes, talk to customers, coordinate with other teams, decide what to build next. Engineering is changing and great engineers are more important than ever.
— Boris Cherny, Claude Code creator, on why Anthropic are still hiring developers
The retreat challenged the narrative that AI eliminates the need for junior developers. Juniors are more profitable than they have ever been. AI tools get them past the awkward initial net-negative phase faster. They serve as a call option on future productivity. And they are better at AI tools than senior engineers, having never developed the habits and assumptions that slow adoption.
The real concern is mid-level engineers who came up during the decade-long hiring boom and may not have developed the fundamentals needed to thrive in the new environment. This population represents the bulk of the industry by volume, and retraining them is genuinely difficult. The retreat discussed whether apprenticeship models, rotation programs and lifelong learning structures could address this gap, but acknowledged that no organization has solved it yet.
— Thoughtworks, findings from a retreat concerning "the future of software engineering", conducted under Chatham House rules